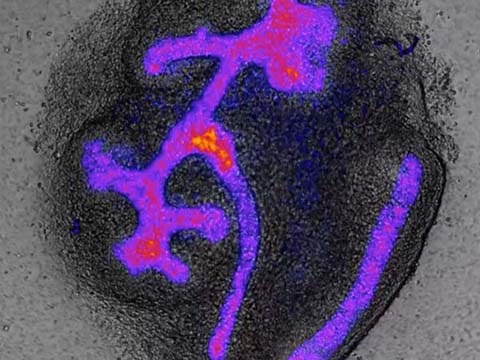
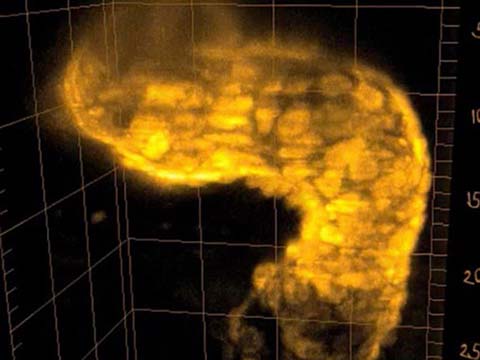
The heart muscle cells of this transgenic fish expresses GCaMP, a genetically encoded fluorescent calcium indicator. Visible is the wave of cardiac conduction, traveling over the heart from atrium (bottom) to ventricle (top left). The heart has a size of about 250 um and beats at a rate of about two times per second. It was imaged in 3D inside the living zebrafish using Selective Plane Illumination Microscopy (SPIM) (Huisken et al. 2004).
2012 Small World In Motion Competition

Honorable Mention
Beating heart of a living 2 day old Danio rerio (zebrafish)
Dr. Michael Weber
- Affiliation
- Max Planck Institute of Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics
Dresden, Saxony, Germany
- Technique
Selective Plane Illumination Microscopy (SPIM)
- Magnification
- 20x
Honorable Mention
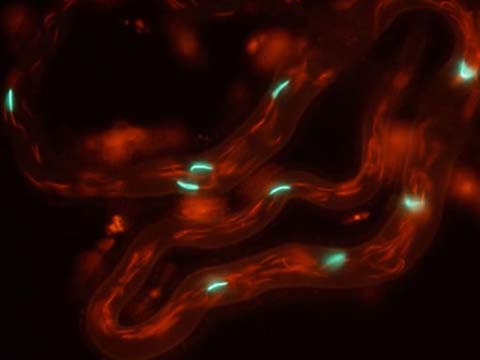
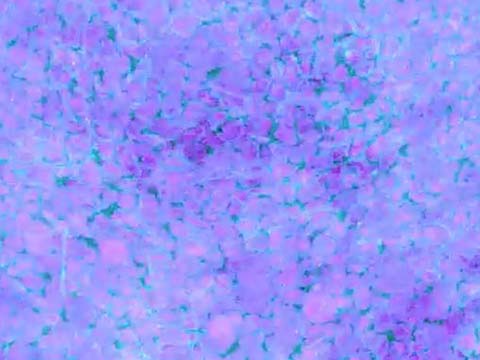
Fast moving endosomes in Arabidopsis thaliana root cells
Dr. Daniel von Wangenheim
- Affiliation
- Goethe University
BMLS - Buchmann Institute for Molecular Life Sciences
Frankfurt am Main, Germany
- Technique
- Light Sheet-based Fluorescence Microscopy
- Magnification
- 63x
A sheet of light is used to illuminate the plant (Arabidopsis thaliana), from the side while collecting the emitted light at a perpendicular axis. The plant grows in an upright position in the microscope’s specimen chamber. While the leaves remain in the air, the root system is perfused with liquid medium. and root stably expresses the early endosome/exosome marker 35S::GFP-RabA1d. The quick endosomes move with up to 10 µm/s, which presents a serious imaging challenge. This technique allows new insides in the dynamics of endosomal compartments in plant cells. The Arabidopsis line was kindly provided by Tobias Berson and Jozef Samaj.
Honorable Mention
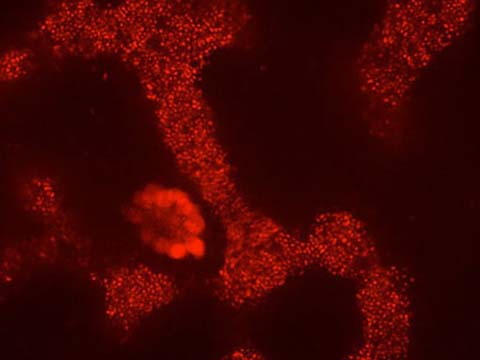
Imaging of the formation of the anterior hindbrain from a flat sheet of neural plate cells in a zebrafish embryo
Fengzhu Xiong
- Affiliation
- Harvard Medical School
Megason Lab
Department of Systems Biology
Boston, Massachusetts, USA
- Technique
- Confocal Time-lapse
- Magnification
- 400x
The video demonstrates the formation of the anterior hindbrain from a flat sheet of neural plate cells in a zebrafish embryo. In particular, we view the patterns of the nervous system, which are important for understanding human disease. Membrane and nuclear fluorescent proteins were used to label the cells.
Top 20
Honorable Mentions



 Share
Share Tweet
Tweet Pin-It
Pin-It